Understanding Pain and Spine Management: A Comprehensive Guide
Chronic pain, especially in the spine, can really affect the quality of one’s life. It is a common problem affecting several million people around the world, which frequently causes a reduction in mobility and functionality, and in extreme conditions, disability. Pain and spine management is a multidisciplinary approach directed toward the diagnosis, treatment, and management of spinal pain. In this article, we shall delve into the causes of spinal pain, its various treatment options, and some preventive tips against spinal pain.

What Causes Spinal Pain?
Spinal pain may be due to many causes, which include:
- Degenerative Disc Disease: This is a disease wherein intervertebral discs, acting like shock absorbers between the bones of the spine, wear down and tear away due to age or injury.
- Herniated Discs: In a herniated disc, the soft inner substance of the spinal disc bulges out through the outer layer, which might press the nerves. It may lead to severe pain, numbness, or limb weakness.
- Spinal Stenosis: Narrowing around the spinal canal may put pressure on the spinal cord and nerves, causing pain, tingling, or muscle weakness.
- Spondylolisthesis: This condition involves the forward slipping of one vertebra over the other, which results in instability and pain; it may be caused by trauma, degeneration, or congenital conditions.
- Osteoarthritis: This is a type of arthritis where the cartilage within the spinal joints will be degraded due to pain and swelling, with reduced motion in the spine.
- Muscle Strains and Sprains: The most common causes of back pain, strain, and sprain injuries are generally due to overuse, bad lifting, and jolting movements.
- Infections and Tumors: Though less common, infections and tumors of the spine may also present with back pain requiring immediate medical attention.
Approaches to Pain and Spine Management
Management of spinal pain is a highly individualized process that encompasses multifaceted components of the patient’s condition and their needs. The following are the major forms of management for spinal pain:
- Medication Management:
Pain management generally begins with medication. Mild to moderate pain may be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers, including acetaminophen and NSAIDs. More severe pain may require stronger prescription medications, such as muscle relaxants, nerve pain medicines, or opioids, which must be carefully monitored by a doctor. - Physical Therapy:
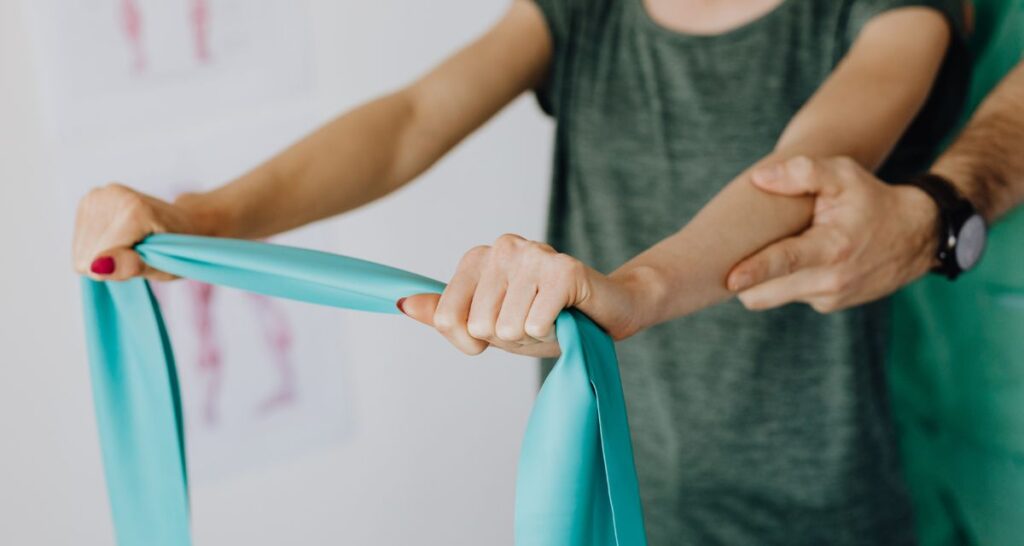
Another cornerstone in managing the spine is physical therapy. An instructed physical therapist can guide a patient through exercises intended for strengthening the muscles around the spine, improving flexibility, and enhancing overall spinal health. This approach will alleviate pain and prevent further injuries. - Chiropractic Care:
Conditions that can respond well to the chiropractic treatment include spinal manipulation, which enhances alignment and function, relieving pain. Some individuals benefit from great pain relief because of chiropractic treatments, while others may not; hence, one has to consult a health professional if it’s appropriate for the condition. - Injections:
Injections are an option mostly for the patients who do not respond to medicine and physical therapy. It may reduce inflammation and pain in the affected area as a result of epidural steroid injections, blocks the nerves, and facet joint injections. - Surgery:
Surgery is often the last resort after other treatments have not yielded good results. Surgical options often depend on what exactly is causing the pain but may include discectomy, where a herniated disk is removed; spinal fusion, which combines two or more vertebrae; or laminectomy, which removes a part of the vertebrae to take pressure off the spinal cord. - Alternative Therapies:
Other methods of alleviating pain for so many patients include alternative therapies such as acupuncture, massage therapy, and yoga. These decrease stress, improve posture, and, in general, promote well-being, which allows pain to resolve. - Lifestyle Modifications:
Weight control, termination of smoking, and exercising are other aspects that play a significant role in the management of spinal pain. A healthy lifestyle reduces stress on the spine and increases general well-being.
Preventing Spinal Pain
While not all spinal pain can be prevented, there are several steps you can take to reduce your risk:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: For people with excess weight, particularly those carrying extra weight around their middles, put added stress on the spine. Maintaining a healthy weight through a proper diet and regular exercise will minimize this strain.
- Practice Good Posture: Over time, bad sitting and standing posture can give rise to spinal pain. Pay attention to your posture, keeping your back straight, your shoulders back, and your feet flat on the floor when sitting.
- Exercise Regularly: Routine exercise, especially of core-strengthening muscles, can help support the spine and reduce the risk of an injury. Swimming, walking, and yoga can be incorporated into your daily routine for better spine health.
- Lift Properly: A person should lift correctly by bending at the knees and keeping the object near the body to avoid straining his or her back.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking enhances the risk of degeneration in the spinal discs. Stopping smoking improves not only spinal health but also general health.
- Stay Hydrated: Plenty of water keeps the spinal discs hydrated to retain their cushioning feature and prevent degeneration.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While most cases of mild to moderate spinal pain can be managed at Rabbetz Sports Chiropractic with rest, over-the-counter medications, and self-care, the following symptoms warrant immediate medical attention:
- Severe, unrelenting pain that does not improve with rest or medications.
- Pain that radiates down the legs or arms.
- Numbness, tingling, or weakness in the limbs.
- Loss of bladder or bowel control.
- Unexplained weight loss, fever, or chills accompanying back pain.
These symptoms could indicate a more serious underlying condition that requires prompt evaluation and treatment.
Conclusion
Pain and spine management is a multifaceted approach that requires a combination of medical interventions, lifestyle changes, and preventive measures. By understanding the causes of spinal pain and exploring the various treatment options available, individuals can make informed decisions about their care and work towards achieving a pain-free life. If you are experiencing spinal pain, consult with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized management plan tailored to your specific needs.