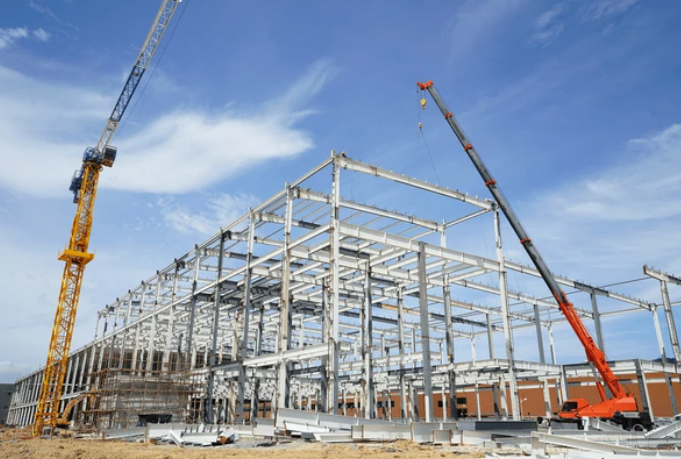
The Resilience and Versatility of Steel Buildings

Introduction:
In the realm of construction and architecture, steel buildings have emerged as a symbol of resilience, durability, and sustainability. The use of steel in construction has transformed the landscape of modern architecture, providing a versatile solution that combines strength with aesthetic appeal. This article delves into the various aspects of steel buildings, exploring their history, benefits, applications, and the environmental impact of this innovative construction material.
History of Steel Buildings:
The use of steel building dates back to the 19th century when the Industrial Revolution sparked significant advancements in metallurgy. The development of the Bessemer process, which allowed for the mass production of steel, marked a turning point in construction history. The Eiffel Tower, completed in 1889, stands as an early example of steel’s potential in architecture, showcasing its strength and flexibility.
Benefits of Steel Buildings:
- Strength and Durability: Steel is renowned for its exceptional strength, making it an ideal material for constructing buildings that can withstand harsh weather conditions, seismic activity, and other external pressures. Steel structures exhibit a high degree of durability, ensuring a longer lifespan compared to traditional construction materials.
- Versatility in Design: Steel’s malleability and strength offer architects and builders unparalleled design freedom. The material allows for the creation of large, open spaces without the need for excessive support columns, enabling innovative and aesthetically pleasing architectural designs.
- Cost-Effectiveness: While the initial cost of using steel in construction may be higher than some traditional materials, the long-term cost benefits are significant. Steel buildings require minimal maintenance, have a longer lifespan, and are resistant to common issues such as rot, pests, and decay.
- Energy Efficiency: Steel buildings can be designed with energy efficiency in mind. They can incorporate insulation materials and reflective roofing that reduce the need for heating and cooling, leading to lower energy consumption and costs.
Applications of Steel Buildings:
- Commercial and Industrial Structures: Steel buildings are widely used in the construction of commercial and industrial facilities. Warehouses, factories, and distribution centers benefit from the expansive spaces that steel structures can provide. The strength of steel also allows for the construction of multi-story buildings, maximizing the use of limited space.
- Residential Construction: Steel has found its way into residential construction, offering homeowners a durable and customizable alternative to traditional building materials. Steel-framed homes are becoming increasingly popular due to their resistance to pests, fire, and adverse weather conditions.
- Infrastructure and Bridges: The infrastructure sector extensively utilizes steel in the construction of bridges and other critical structures. The material’s high strength-to-weight ratio makes it an ideal choice for creating durable and efficient transportation infrastructure.
- Agricultural Buildings: Farmers and agricultural businesses benefit from the versatility of steel buildings. Barns, storage facilities, and equipment shelters constructed with steel provide a robust solution for protecting assets from the elements.
Versatility in Design and Construction
Steel buildings are renowned for their versatility in design and construction. Unlike traditional building materials like wood or concrete, steel offers greater flexibility in shaping architectural designs.
Architects and designers appreciate the freedom that steel provides in creating innovative and modern structures. Whether it’s a sleek office building, a contemporary residential home, or a sprawling industrial complex, steel can be tailored to meet various aesthetic and functional requirements.
Moreover, steel buildings are highly customizable, allowing for easy integration of features like windows, doors, insulation, and interior finishes. This adaptability makes steel an ideal choice for projects with specific design specifications and customization needs.
Environmental Impact:
- Recyclability: One of the key environmental advantages of steel is its recyclability. Steel is the most recycled material globally, with the ability to be reused without losing its inherent properties. This significantly reduces the environmental impact associated with the extraction and production of new materials.
- Energy Efficiency: Steel buildings can be designed to be energy-efficient, contributing to overall sustainability efforts. By incorporating features such as efficient insulation and reflective roofing, steel structures can reduce energy consumption and decrease the environmental footprint over their lifespan.
- Reduced Waste: The precision involved in manufacturing steel components leads to minimal on-site waste during construction. Additionally, the longevity of steel buildings means fewer demolitions and less waste generated compared to structures built with less durable materials.
Conclusion:
Steel buildings have evolved from being a symbol of industrial might to becoming a cornerstone of modern architecture. The inherent strength, versatility, and environmental sustainability of steel make it a preferred choice for construction projects across various sectors. As technology advances and architectural trends continue to evolve, steel’s adaptability ensures its continued prominence in the construction industry. for blog to visit site hituponviews.