Smart Cities and Energy Management rapid urbanization
Introduction
In the wake of rapid urbanization and environmental concerns, Smart Cities are emerging as beacons of innovation, particularly in the realm of energy management. This article delves into how Smart Cities leverage advanced technologies to revolutionize energy consumption, promote sustainability, and create more efficient urban ecosystems.
Smart Infrastructure for Efficiency
Smart Cities employ a comprehensive approach to energy management, starting with the development of intelligent infrastructure. Automated systems, sensor networks, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices are strategically integrated to monitor and optimize energy consumption across various sectors, including transportation, buildings, and public services.
Data-Driven Decision Making
At the core of Smart Cities’ energy management strategy is the collection and analysis of vast amounts of data. Advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms process real-time data from sensors and devices, providing city planners with insights into energy usage patterns. This data-driven approach enables informed decision-making for optimizing energy efficiency.
Smart Building Technologies
Smart Cities prioritize energy-efficient buildings through the implementation of smart technologies. Automated systems control lighting, heating, and cooling based on occupancy and external conditions. Additionally, smart meters and sensors enable real-time monitoring, allowing residents and businesses to make informed decisions about their energy usage.
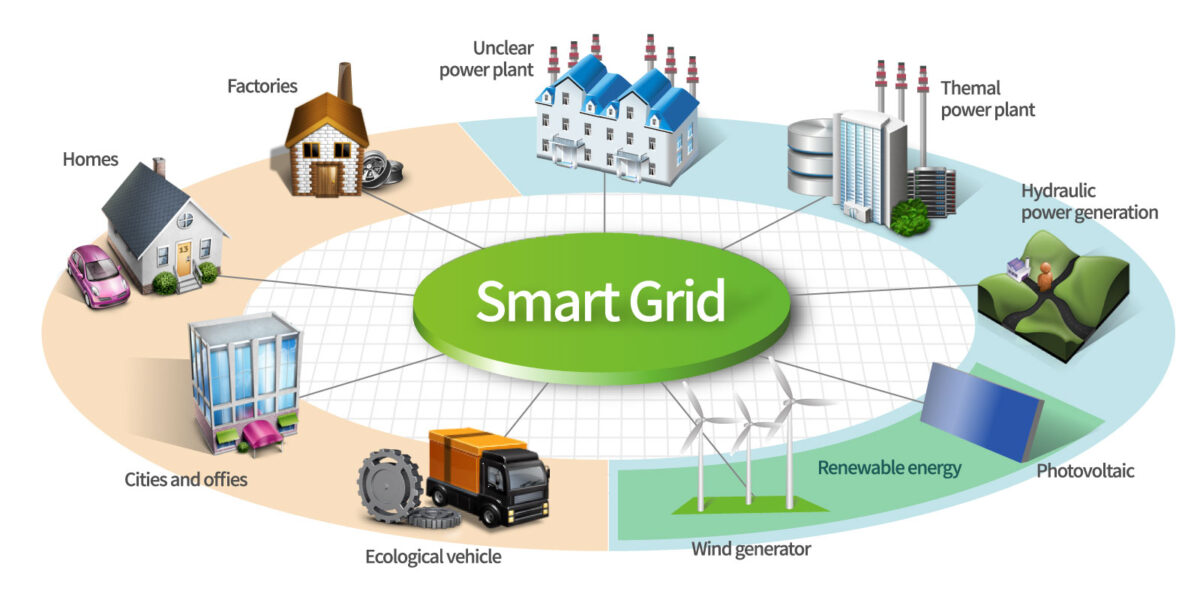
Renewable Energy Integration
To reduce dependence on traditional energy sources, Smart Cities embrace renewable energy integration. Solar panels, wind turbines, and other sustainable technologies are integrated into the urban landscape to harness clean energy. These initiatives contribute not only to environmental conservation but also to the resilience of the city’s energy grid.
Intelligent Traffic Management
Smart transportation systems play a pivotal role in energy management. Intelligent traffic management systems optimize traffic flow, reducing congestion and idling times. This not only enhances the efficiency of transportation but also minimizes fuel consumption and associated emissions.
Promoting Sustainable Mobility
Smart Cities prioritize sustainable modes of transportation, including electric vehicles, bike-sharing programs, and efficient public transit systems. By encouraging green transportation options, cities aim to reduce the carbon footprint of commuting, contributing to cleaner air and a healthier urban environment.
Dynamic Energy Pricing
Smart Cities implement dynamic energy pricing models to incentivize energy consumption during off-peak hours. This approach encourages consumers to shift their energy usage to times when demand is lower, reducing the strain on the energy grid during peak hours.
Demand Response Programs
Demand response programs utilize real-time data to adjust energy consumption based on demand fluctuations. Automated systems can temporarily reduce energy usage in non-critical areas during peak demand, preventing grid overload and ensuring a more stable and efficient energy supply.
Data Privacy and Security
As Smart Cities rely heavily on data for energy management, ensuring the privacy and security of this information is paramount. Robust cybersecurity measures must be in place to safeguard sensitive data and protect against potential threats or breaches.
Infrastructure Investment
The transition to Smart City energy management requires significant infrastructure investment. Upgrading existing systems and implementing new technologies can be costly, and cities must carefully plan and allocate resources to ensure a smooth and sustainable transition.
Continual Technological Advancements
The future of Smart Cities and energy management holds exciting prospects with continual technological advancements. Artificial intelligence, advanced sensors, and improved energy storage solutions are anticipated to further enhance the efficiency and sustainability of urban energy systems.
Global Collaboration for Sustainable Development
As the concept of Smart Cities gains momentum globally, collaboration between cities becomes essential. Sharing best practices, technologies, and strategies for sustainable urban development can accelerate progress and contribute to a collective effort in mitigating the environmental impact of urbanization.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Smart Cities are at the forefront of redefining urban living through innovative energy management practices. By integrating smart technologies, data-driven decision-making, and sustainable energy solutions, these cities pave the way for a more efficient, resilient, and environmentally conscious urban future.
FAQs
How do Smart Cities optimize energy use in buildings?
Smart Cities optimize energy use in buildings through the implementation of smart technologies, including automated systems for lighting, heating, and cooling, as well as real-time monitoring using smart meters and sensors.
What role does renewable energy play in Smart Cities?
Smart Cities integrate renewable energy sources such as solar panels and wind turbines to reduce dependence on traditional energy sources. This contributes to environmental conservation and enhances the resilience of the city’s energy grid.
How do Smart Cities promote sustainable transportation?
Smart Cities promote sustainable transportation through intelligent traffic management systems, the prioritization of electric vehicles, bike-sharing programs, and efficient public transit systems, aiming to reduce the carbon footprint of commuting.
What are demand response programs in Smart City energy management?
Demand response programs in Smart Cities use real-time data to adjust energy consumption based on demand fluctuations. Automated systems temporarily reduce energy usage in non-critical areas during peak demand, ensuring a stable and efficient energy supply.