How to Choose the Right Materials in Millwork Drafting
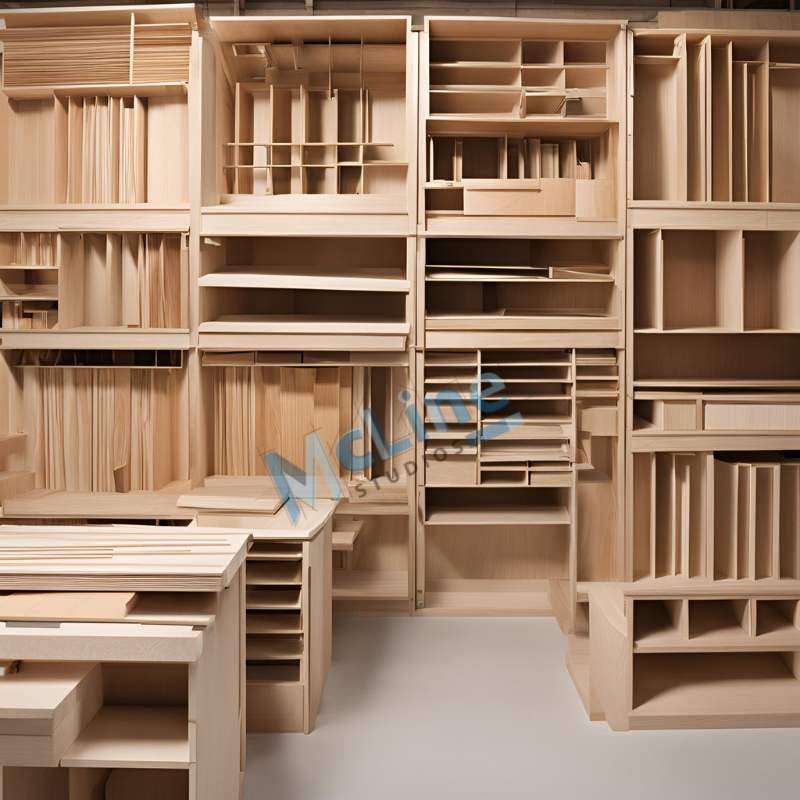

Millwork drafting is a specialized field within interior design and architecture that focuses on the detailed drawing and specification of custom woodwork and cabinetry. This process involves creating precise, scaled drawings that illustrate how various elements like cabinets, moldings, trims, and other wooden fixtures should be constructed and installed.
Selecting the appropriate materials for millwork Drafting is crucial because it directly affects the durability, aesthetics, and functionality of the final product. High-quality materials ensure that the millwork will withstand daily wear and tear, maintaining its appearance and structural integrity over time.
The choice of materials also influences the visual appeal of the millwork, allowing for a range of finishes, textures, and colors that can complement the overall design of the space.
Understanding Millwork Drafting Materials
Understanding millwork drafting materials involves knowing the different types of materials used in the creation of custom woodwork, such as trim, molding, cabinetry, and furniture. Here’s a detailed look at the main millwork materials:
1 Solid Wood
Characteristics: Natural, durable, and can be refinished.
Types: Hardwood (e.g., oak, maple, cherry, walnut): Strong, dense, and ideal for high-quality furniture and cabinetry.
Softwood (e.g., pine, cedar, spruce): Lighter, more workable, and often used for trim and decorative elements.
2. Engineered Wood Products
Plywood: Made from thin layers of wood veneer glued together, offering strength and stability.
Medium-Density Fiberboard (MDF): Made from wood fibers bonded with resin, smooth and uniform, often used for painted finishes.
Particleboard: Made from wood particles and resin, less expensive but not as strong as plywood or MDF.
3. Veneers
Characteristics: Thin slices of wood applied to the surface of furniture or cabinetry, providing the appearance of solid wood.
Advantages: Cost-effective, can create unique patterns, and reduces the need for solid wood.
4. Laminates
Characteristics: Layers of paper or fabric impregnated with resin and bonded to a substrate like MDF or particleboard.
Types:
High-Pressure Laminate (HPL): Durable and resistant to scratches and heat.
Low-Pressure Laminate (LPL): Less durable but more affordable.
5. Composite Materials
Characteristics: Made from a mixture of wood fibers, plastics, and other materials.
Uses: Often used for outdoor furniture, trim, and flooring due to their resistance to moisture and decay.
6. Plastics and Acrylics
Characteristics: Lightweight, versatile, and can mimic the appearance of wood or other materials.
Uses: Common in modern cabinetry and furniture design for a sleek, contemporary look.
7. Metals
Characteristics: Strong, durable, and often used in conjunction with other materials for structural support or decorative elements.
Types:
Aluminum: Lightweight and corrosion-resistant.
Steel: Strong and durable, often used in structural applications.
Brass and Copper: Used for decorative accents due to their aesthetic appeal.
8. Glass
Characteristics: Transparent or translucent, used to add visual interest and lightness to millwork.
Types:
Tempered Glass: Heat-treated for strength and safety.
Frosted or Etched Glass: Used for privacy and decorative purposes.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Materials
Choosing the right materials is crucial in various fields such as construction, manufacturing, and product design. Here are some key factors to consider when making decisions about materials:
1. Project Requirements and Specifications
Functionality and Use
Consider the intended use of the millwork (e.g., cabinetry, trim, furniture).
Assess the functional needs such as load-bearing capacity, moisture resistance, and thermal insulation.
Determine if the material needs to meet specific performance criteria (e.g., fire resistance, acoustic properties).
Aesthetic Preferences
Identify the desired look and feel of the finished product.
Match material choices with the overall design theme (e.g., traditional, modern, rustic).
Consider color, grain patterns, and texture to achieve the desired aesthetic outcome.
2. Budget Constraints
Initial Cost vs. Long-term Investment
Evaluate the upfront cost of materials versus their lifespan and maintenance costs.
Consider if investing in higher-quality materials may save money in the long run through durability and less frequent repairs.
Material Cost Variations
Research the cost range of different materials to find options that fit within the budget.
Balance the quality and cost to ensure the best value for money.
3. Durability and Longevity
Resistance to Wear and Tear
Choose materials that can withstand daily use and potential impacts.
Consider the material’s resistance to scratches, dents, and other forms of damage.
Maintenance Needs
Assess how much maintenance the material will require over its lifespan.
Opt for materials that are easy to clean and maintain if low maintenance is a priority.
4. Environmental and Sustainability Concerns
Eco-friendly Materials
Look for materials that are sustainably sourced and have a low environmental impact.
Consider using reclaimed or recycled materials where possible.
Certifications
Check for certifications such as FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) to ensure the materials are responsibly sourced.
Consider materials with low VOC (Volatile Organic Compounds) emissions to improve indoor air quality.
5. Availability and Supply Chain Considerations
Local vs. Imported Materials
Evaluate the pros and cons of sourcing materials locally versus importing them.
Local materials may be more cost-effective and have shorter lead times, while imported materials might offer unique qualities or aesthetics.
Lead Times and Supply Reliability
Consider the availability of materials and potential delays in the supply chain.
Ensure that chosen materials can be sourced consistently and in the required quantities to avoid project delays.
6. Aesthetic and Design Considerations
Matching Existing Structures
Ensure new millwork drafting materials are compatible with existing elements in the space.
Harmonize colors, textures, and styles for a cohesive look.
Flexibility and Customization
Choose materials that can be easily shaped, cut, and finished to meet design specifications.
Consider how well the material can be customized to achieve the desired details and intricacies.
7. Technical Specifications and Standards
Compliance with Codes and Regulations
Verify that materials meet local building codes and safety standards.
Consider any industry standards that may apply to specific types of millwork.
Performance in Specific Conditions
Assess how materials perform in the specific environment where they will be used (e.g., high humidity areas, outdoor use).
Ensure materials are suitable for the climate and conditions they will be exposed to.
8. Innovations and New Technologies
Advanced Material Options
Explore new materials and technologies that offer superior performance or unique benefits.
Stay updated on innovations in millwork materials that could enhance the project.
Integration with Modern Techniques
Consider how new materials can be integrated with modern construction and fabrication techniques.
Evaluate the compatibility of materials with digital drafting and CNC machining processes.

Follow for more Article
Comparing Material Options
Comparing material options involves evaluating various factors to determine the most suitable choice for a specific application or project. Here’s a structured approach to comparing materials:
1. Pros and Cons of Different Woods
Hardwoods
Examples: Oak, Maple, Cherry, Walnut
Pros:
Durability: Hardwoods are generally more durable and resistant to dents and scratches.
Aesthetic Appeal: Rich, natural grain patterns and colors add a premium look.
Longevity: High longevity with proper care.
Cons:
Cost: Typically more expensive than softwoods.
Workability: Harder to cut and shape due to de
2. Engineered Woods
Plywood
Pros:
Strength: Strong and stable due to its cross-grained structure.
Versatility: Available in various grades and finishes for different applications.
Cost: Generally more affordable than solid wood.
Cons:
Aesthetic: Edges need to be covered for a finished look.
Moisture Sensitivity: Prone to damage if exposed to moisture over time.
3. Veneers and Laminates
Veneers
Pros:
Aesthetic: Provides the look of solid wood at a lower cost.
Sustainability: Uses less wood than solid lumber.
Versatility: Can be applied to a variety of substrates.
Cons:
Durability: The thin surface can be damaged easily.
Complexity: Requires skilled application to avoid bubbling and peeling.
4. Alternative Materials
Metals
Pros:
Durability: Extremely strong and long-lasting.
Modern Aesthetics: Provides a sleek, contemporary look.
Cons:
Cost: Can be expensive, especially for custom designs.
Workability: Requires specialized tools and skills.
Conclusion
In conclusion, selecting the right materials for millwork drafting is essential for achieving durable, functional, and aesthetically pleasing woodwork. Understanding the characteristics and applications of solid wood, engineered wood products, veneers, laminates, composite materials, plastics, metals, and glass is crucial.
Factors such as project requirements, budget constraints, durability, environmental considerations, availability, aesthetic goals, and technical specifications must all be evaluated.
By carefully balancing these factors, designers can ensure that the chosen materials meet the needs of the project while also fitting within the overall design vision.
Advances in materials and technologies continue to expand the possibilities for innovative and sustainable millwork solutions, enhancing both the performance and visual appeal of custom woodwork in interior spaces.