What Is the Difference Between an ECG and an Echocardiogram?
Cardiovascular health is a cornerstone of overall well-being, and modern medicine offers numerous tools to assess heart function. Two of the most commonly used diagnostic tests are the electrocardiogram (ECG) and the echocardiogram. Although they are often mentioned together, they serve different purposes and provide distinct insights into heart health. Understanding their differences can help patients feel more informed and comfortable during their medical journey. This article delves into the unique characteristics of ECGs and echocardiograms, highlighting their roles, processes, and what they reveal about the heart.
Understanding the Basics What Is an ECG?
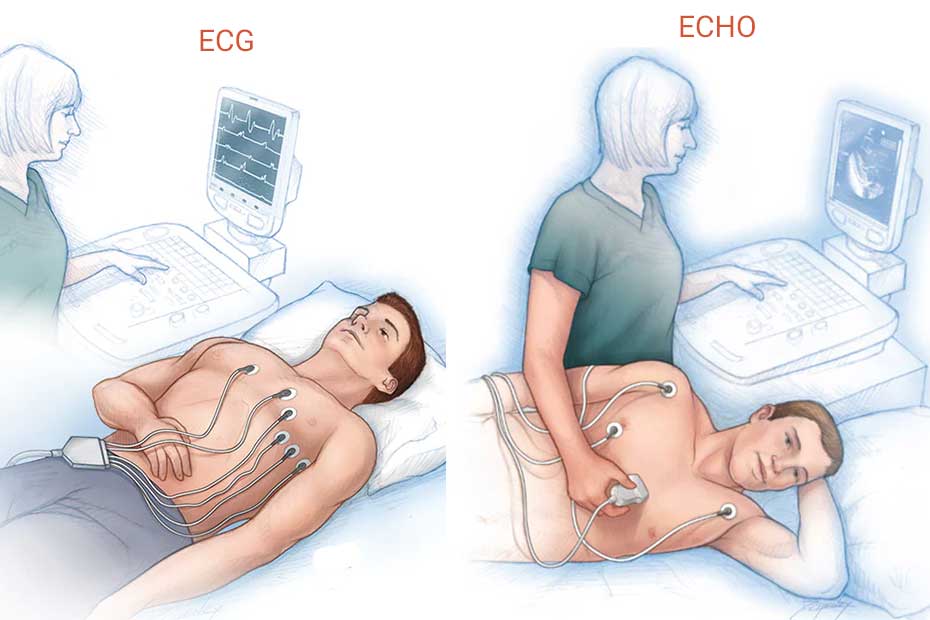
An electrocardiogram, or ECG, is a test that measures the electrical activity of the heart. The heart’s rhythm and electrical impulses are essential indicators of its health and function. By attaching small electrodes to the skin on the chest, arms, and legs, an ECG records the heart’s electrical signals and displays them as waves on a monitor or paper, ECG in Dubai.
How Does an ECG Work?
The heart generates tiny electrical impulses that trigger its contraction, enabling it to pump blood throughout the body. An ECG captures these impulses and presents them as a series of wave-like patterns, each representing a different phase of the heart’s cycle. These patterns can indicate whether the heart is beating too fast, too slow, or irregularly, and can also reveal signs of previous heart attacks or other abnormalities.
What Does an ECG Reveal?
- Heart Rhythm and Rate: It shows whether the heart is beating normally, or if there are any arrhythmias.
- Heart Attacks: It can detect signs of a previous heart attack or one currently happening.
- Electrolyte Imbalances: Variations in the ECG can signal issues such as potassium or calcium imbalances.
- Structural Abnormalities: While limited, ECGs can sometimes suggest problems like enlarged heart chambers.
Understanding the Basics: What Is an Echocardiogram?
An echocardiogram Test in Dubai, often simply called an “echo,” is a type of ultrasound that visualizes the heart’s structure and function. By using sound waves, this test produces detailed images of the heart, including its chambers, valves, and blood flow. It’s an excellent tool for evaluating the mechanical aspects of heart health.
How Does an Echocardiogram Work?
During an echocardiogram, a technician or doctor places a transducer on the patient’s chest. This device emits sound waves that bounce off the heart’s structures and return to the transducer. A computer then translates these reflected waves into moving images displayed on a screen.
What Does an Echocardiogram Reveal?
- Heart Size and Shape: It shows if the heart or its chambers are enlarged.
- Valve Function: It can detect problems with the heart valves, such as stenosis or regurgitation.
- Heart Muscle Movement: It reveals how well the heart muscle is contracting and if any parts of the heart are not functioning properly.
- Blood Flow: It can assess blood flow through the heart and major arteries, helping to detect clots, tumors, or other abnormalities.
Key Differences Between an ECG and an Echocardiogram
While both tests are essential in diagnosing and monitoring heart conditions, they differ significantly in their methodologies, the information they provide, and their clinical uses.
1. Nature of the Test
- ECG: Measures the heart’s electrical activity.
- Echocardiogram: Visualizes the heart’s physical structure and movement.
2. Purpose of the Test
- ECG: Ideal for detecting arrhythmias, heart attacks, and electrical abnormalities.
- Echocardiogram: Used to evaluate heart size, shape, valve function, and blood flow.
3. Procedure
- ECG: Non-invasive, quick, and simple. Electrodes are attached to the skin, and the test takes just a few minutes.
- Echocardiogram: Non-invasive but more complex. It involves using a transducer and may take up to 30-60 minutes.
4. Output
- ECG: Produces a graph of electrical activity, interpreted as waves and intervals.
- Echocardiogram: Generates moving images of the heart, allowing visual assessment of its structure and function.
5. Use Cases
- ECG: Commonly used for routine check-ups, emergency diagnosis of heart attacks, and monitoring known heart conditions.
- Echocardiogram: Often ordered to investigate heart murmurs, assess heart function after a heart attack, or monitor chronic heart diseases like heart failure.
Which Test Is Right for You?
The choice between an ECG and an echocardiogram depends on what information your doctor needs. For issues related to heart rhythm or when suspecting a heart attack, an ECG is typically the first step. If there’s a need to understand the heart’s structure, function, or blood flow, an echocardiogram provides a more comprehensive picture.
Conclusion
Both ECGs and echocardiograms play crucial roles in diagnosing and managing heart health. While an ECG focuses on the heart’s electrical activity, an echocardiogram provides a detailed view of its physical structure and function. Understanding their differences can empower patients to engage more confidently in discussions about their health and treatment options.
FAQs
1. Can an ECG and an echocardiogram be performed together?
Yes, these tests can be complementary. An ECG provides information about the heart’s electrical activity, while an echocardiogram offers a visual assessment. Together, they give a more complete picture of heart health.
2. Are there any risks associated with these tests?
Both ECGs and echocardiograms are safe, non-invasive procedures. An ECG involves attaching electrodes to the skin, which may cause mild irritation for some people. An echocardiogram uses ultrasound waves and poses no known risks.
3. How should I prepare for an ECG or echocardiogram?
For an ECG, no special preparation is needed. For an echocardiogram, you may be asked to avoid eating or drinking a few hours before the test, especially if a transesophageal echo is planned.
4. Can these tests detect all heart conditions?
No single test can detect all heart conditions. ECGs and echocardiograms are essential tools, but other tests like stress tests, cardiac MRIs, or CT scans may be needed for a comprehensive evaluation.
5. How long do the results take?
Results from an ECG are usually available immediately. Echocardiogram results may take a bit longer, especially if a detailed analysis is required by a cardiologist.







